
By default, these objects are anchored to the wall and remain with the wall if you move it. When you add doors, windows, door/window assemblies, and openings to a wall, the wall automatically adjusts to accommodate the object and adds endcaps where needed. You can also reverse the direction of a wall. The wall direction grip indicates the wall direction.

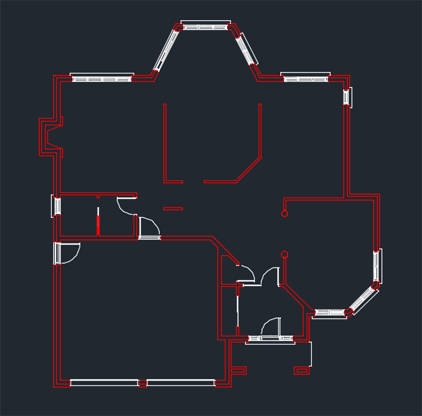
After placing a wall, you can determine the wall direction by selecting the wall. Sample wall styles provided with AutoCAD Architecture were created with the intent that you place perimeter walls in clockwise fashion. Wall direction is significant for some modifications to walls. A wall can have both straight and curved segments. When you add a wall to a drawing, you select a wall tool and then specify the points that define each wall segment. You can also work with casework wall styles that include counters, base units, and upper units. Catalogs provided with AutoCAD Architecture include sample wall styles for common wall types, such as concrete walls with footings or furring, CMU and brick cavity walls, and various stud partition walls. With wall styles, you can specify components, endcaps, materials, and other characteristics to create new types of walls, such as concrete walls, masonry walls, and brick cavity walls (see Figure 1). Wall styles control the appearance of wall objects. The components of walls can also have modifiers, which change the shape of the component or its surface. Some components include brick, CMU, concrete, studs, air gaps, and insulation. A wall has one or more components, which are the materials used to construct the wall. You can create very simple wall types that rely on standard settings and add them on the fly. Walls are the basic components of any building plan. The wall object contains all the geometry needed to represent a wall in 2-dimensional (2D) and 3-dimensional (3D) views. In AutoCAD® Architecture, a wall is an AEC object that represents the real-world features of an interior or exterior wall.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
